We independently review our recommendations, and we may earn commissions from provided links. Find out more.
How to Prevent Muscle Cramps: 9 Extraordinary Methods

By Rashko Arnaudov/ Last Updated January 9, 2024
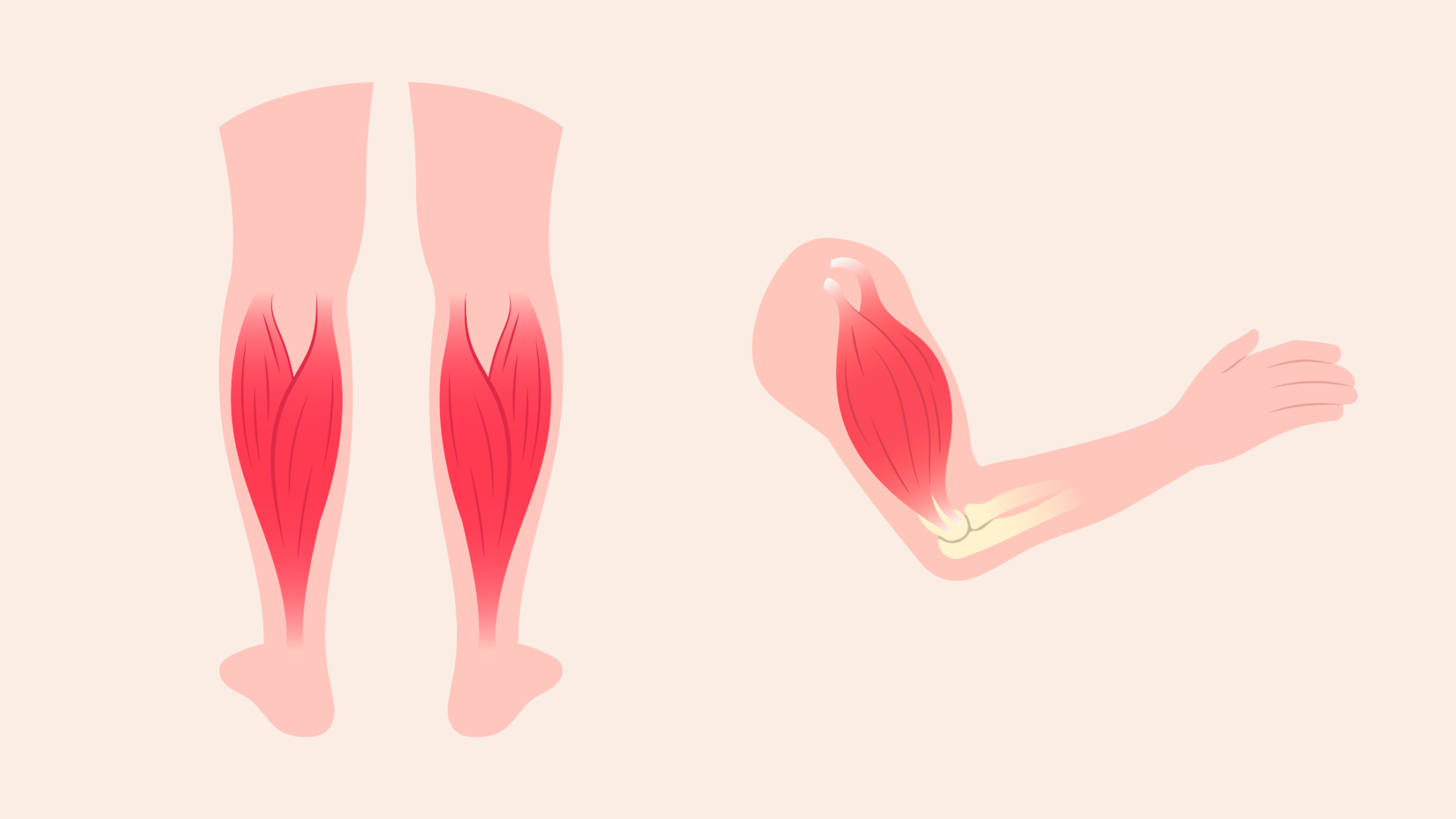
Muscle cramps are involuntary contractions of muscles that can result in discomfort, pain, and temporary loss of muscle control. These episodes often occur suddenly and can range from mildly irritating to intensely painful. This is why people must know how to prevent muscle cramps. While cramps can happen anywhere in the body, they most commonly affect the skeletal muscles, which are under voluntary control.
The exact cause of muscle cramps is not always clear, but several factors are believed to contribute to their occurrence. Dehydration, electrolyte imbalances (such as low levels of potassium, calcium, or magnesium), muscle fatigue, and overexertion during physical activity are common triggers for cramps. Additionally, certain medical conditions, medications, and inadequate stretching before exercise can increase the likelihood of experiencing muscle cramps.
Certain muscle groups are more prone to cramping, and these occurrences often target areas such as the calf muscles (gastrocnemius), muscles in the foot, quadriceps (front of the thigh), and hamstrings (back of the thigh). Individuals engaged in vigorous physical activities, athletes, and those with muscle imbalances or inadequate warm-up routines may be more susceptible to muscle cramps.
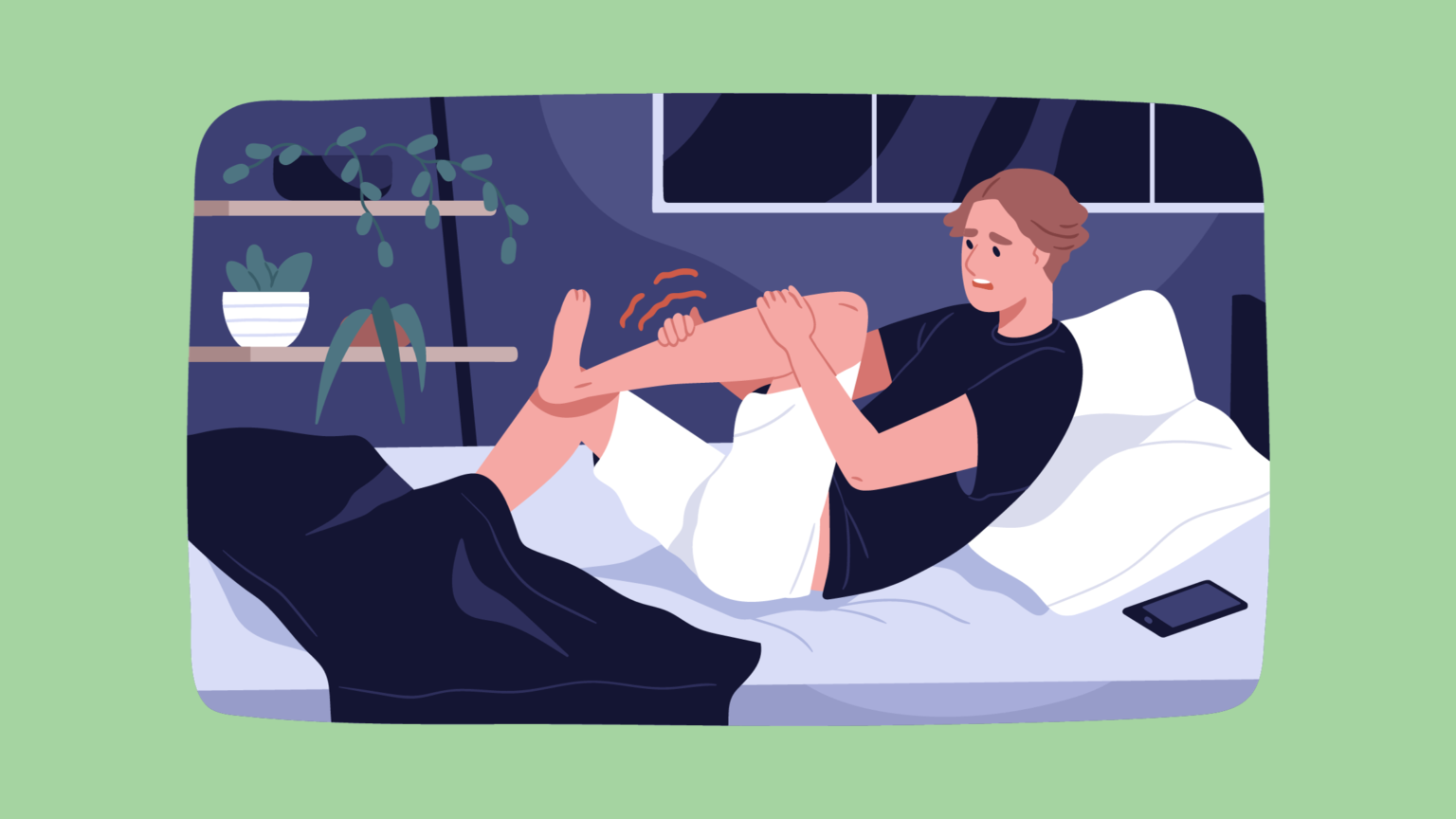

How To Prevent Muscle Cramps?
Preventing muscle cramps involves adopting proactive measures to address various contributing factors. Here are some effective strategies to minimize the occurrence of cramps:
Drink and Eat these foods and drinks
Bananas:
Bananas are effective in preventing muscle cramps due to their high potassium content. Potassium is a vital electrolyte that supports proper muscle function, facilitating nerve signals, and aiding muscle contraction and relaxation. Maintaining optimal potassium levels helps prevent the involuntary muscle contractions characteristic of cramps.
Additionally, bananas contribute to natural hydration, making them a convenient and portable snack for supporting overall muscle health. Incorporating bananas into the diet, along with a balanced intake of electrolytes and proper hydration, can be a practical and beneficial strategy for minimizing the risk of muscle cramps.
Watermelon:
Watermelon, with its high water content, provides excellent hydration, a key factor in preventing muscle cramps. While not as rich in potassium as bananas, watermelon contains L-citrulline, which may aid muscle recovery and reduce soreness. It also offers vitamins A and C, plus antioxidants, promoting overall muscle health. As a low-calorie snack, watermelon is a hydrating and refreshing option that contributes to a balanced diet, potentially reducing the risk of muscle cramps when combined with other potassium-rich foods.
Orange Juice:
Orange juice can contribute to preventing muscle cramps due to its beneficial nutrient profile. It is a rich source of potassium, a vital electrolyte that supports proper muscle function. Potassium helps regulate fluid balance within cells, facilitating smooth muscle contractions and reducing the risk of cramps. Additionally, orange juice provides a good dose of vitamin C, an antioxidant that supports overall muscle health. Including orange juice in your diet, especially before or after physical activity, can help maintain electrolyte balance and reduce the likelihood of muscle cramps.
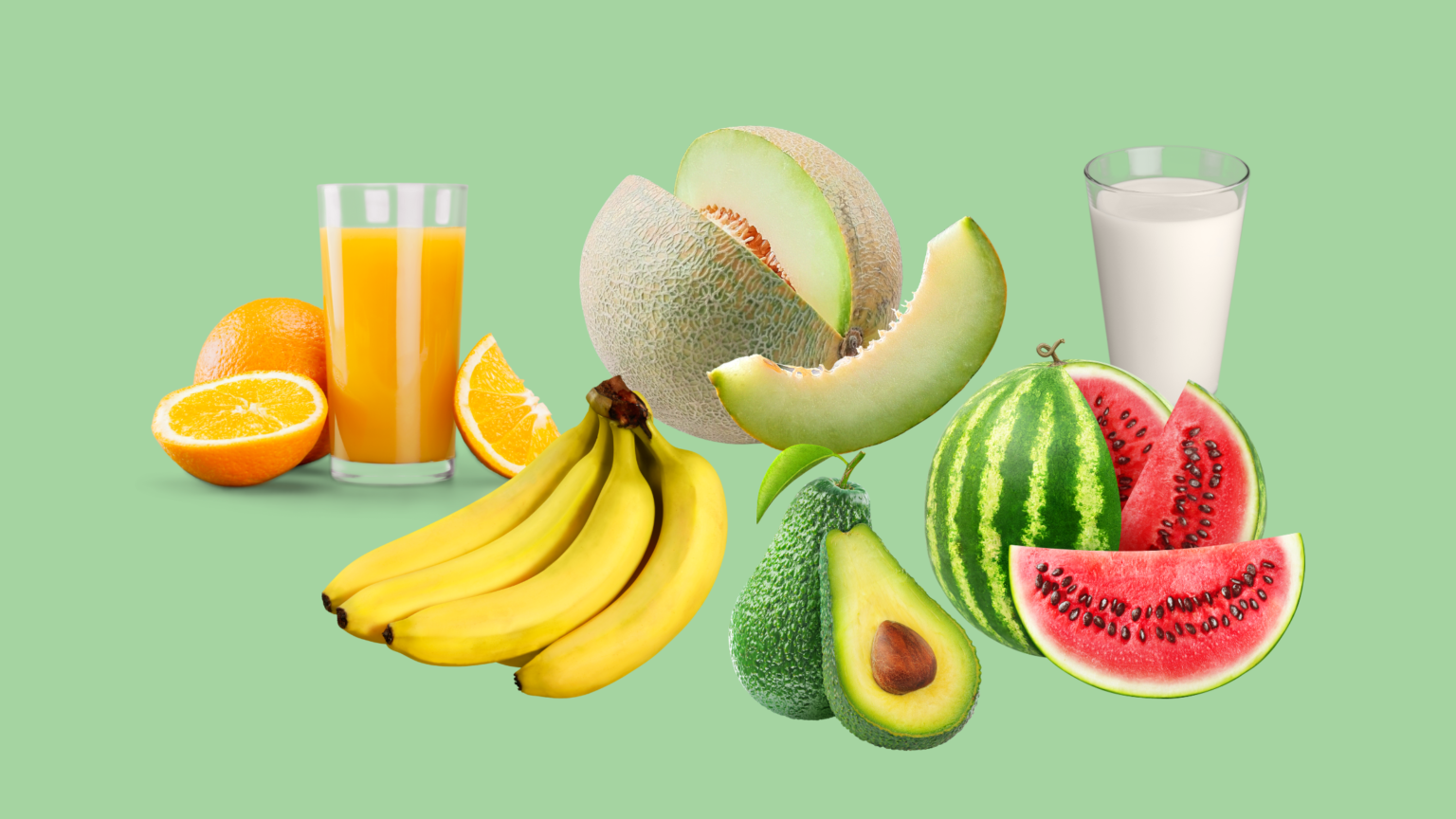

Milk:
Milk is effective in preventing muscle cramps due to its nutrient composition. It is a good source of calcium, potassium, and magnesium, essential minerals that play key roles in muscle contraction and relaxation. Calcium is crucial for muscle function, while potassium and magnesium help maintain electrolyte balance. Including milk in your diet provides these essential nutrients, supporting overall muscle health and reducing the risk of cramps. Additionally, the protein content in milk aids in muscle recovery after exercise, further contributing to preventing cramps.
Avocado:
Avocado can be beneficial in preventing muscle cramps due to its nutrient content. Avocados are rich in potassium, a crucial electrolyte that supports proper muscle function. Potassium helps maintain the balance of fluids in and out of cells, facilitating smooth muscle contractions and reducing the likelihood of cramps. Additionally, avocados provide magnesium, another essential mineral that plays a role in muscle health. Including avocados in your diet contributes to maintaining optimal electrolyte balance, supporting overall muscle function, and helping prevent muscle cramps.
Melon:
Melons, such as watermelon, play a role in preventing muscle cramps for several reasons. Firstly, their high water content contributes to hydration, maintaining fluid balance, and preventing electrolyte imbalances—a common trigger for cramps. Furthermore, melons contain L-citrulline, an amino acid associated with potential benefits for muscle recovery. Although more research is needed, L-citrulline enhances blood flow, supporting overall muscle function and reducing the likelihood of cramps.
Melons also provide essential vitamins and antioxidants, including vitamins A and C, contributing to muscle health and helping combat oxidative stress that may lead to muscle fatigue and cramping.
Warm up and stretch
Engaging in a thorough warm-up and incorporating stretching routines has been a game-changer for me in preventing those uncomfortable muscle cramps during physical activity. The warm-up phase gradually increases blood flow to my muscles, elevates my core temperature, and readies my cardiovascular system for more intense activity. This gradual transition from rest to activity significantly reduces the risk of cramps that might be triggered by sudden and intense exertion.
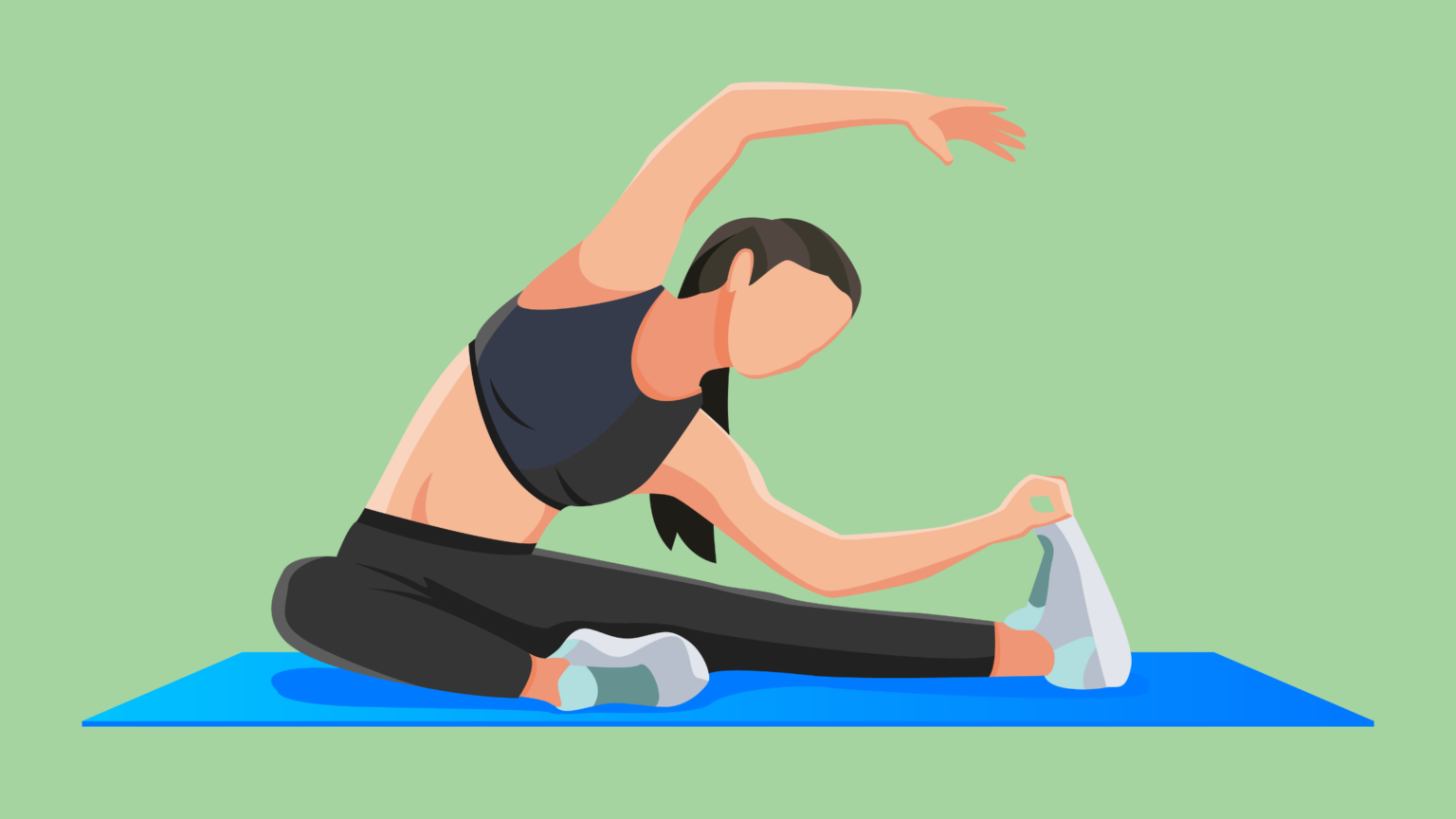

When it comes to stretching, especially dynamic stretching, I’ve found it to be an essential component in my cramp-prevention toolkit. Dynamic stretches involve controlled movements that mimic the activity to follow, enhancing my flexibility and increasing the range of motion in my joints. This type of stretching primes my muscles, making them more responsive and reducing the likelihood of cramps during exercise.
After the workout, incorporating some static stretching during the cool-down phase has proven beneficial. Holding those stretches helps with muscle relaxation, contributing to the prevention of post-exercise cramps and stiffness.
Get Moving
Firstly, initiating movement through activities like a dynamic warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles. This enhanced circulation ensures that muscles receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, promoting optimal function and reducing the likelihood of cramps.
Secondly, getting moving raises the core body temperature. This is essential for preparing the cardiovascular system for the upcoming exertion, helping to transition muscles from a resting to an active state. This gradual transition is effective in minimizing the risk of cramps that can be triggered by sudden and intense efforts.

Moreover, the act of getting moving actively engages the muscles, making them more pliable and responsive. Enhanced flexibility is critical in preventing cramps during and after exercise, as it reduces the likelihood of muscle fibers contracting involuntarily.
Incorporating movement into your pre-exercise routine not only physically prepares your muscles but also contributes to mental readiness. It establishes a mind-body connection, ensuring that your muscles are tuned in and ready for the demands of the impending activity.
Be Hydration
Proper hydration is a foundational element in preventing muscle cramps during physical activity. Adequate water intake helps maintain the crucial balance of electrolytes, such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium, essential for optimal muscle function. An imbalance in these electrolytes, often aggravated by dehydration, can increase muscle excitability and the likelihood of cramps.

Dehydration also leads to reduced blood volume and thicker blood consistency, impairing the efficient transport of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles. This limitation in nutrient supply increases the vulnerability to cramps, particularly during intense physical activity.
Additionally, hydration plays a vital role in thermoregulation, aiding the body in dissipating heat generated during exercise. Elevated body temperature, often a consequence of dehydration, can contribute to muscle fatigue and cramping. Maintaining optimal hydration levels assists in regulating body temperature, reducing stress on muscles, and lowering the risk of cramps.
Apply Heat
Numerous fitness professionals, including personal trainers, coaches, and physical therapists, advocate for the application of magnesium externally, suggesting the utilization of Epsom salts as a means to harness its benefits for the body.
Experiment with a traditional solution by saturating a cloth with it and gently applying it to the contracted muscle. Alternatively, enhance your relaxation by incorporating a generous amount of this remedy into a warm bath for an indulgent soak.

For those seeking alternative approaches, dry heat, exemplified by the use of a heating pad, has proven to be effective. There is a plethora of options available online, offering a range of choices to suit individual preferences.
Begin by setting the heating pad at its lowest temperature, adjusting it only if the desired relief isn’t achieved. This gradual approach allows for a customized experience based on personal comfort levels.
However, it’s crucial to consider certain health conditions, such as diabetes, a spinal cord injury, or any other ailment affecting heat sensitivity. In such cases, using a heating pad may not be advisable, necessitating a careful evaluation of alternative methods for muscle relief.
Reduce stress
Reducing stress is a pivotal strategy in preventing cramps as stress has a direct impact on the body’s physiological responses, including muscle tension and hormonal fluctuations. When stress levels are high, the body releases stress hormones such as cortisol, which can contribute to increased muscle tension. This heightened tension can lead to cramps and muscle spasms, particularly in areas prone to tightness.
Moreover, stress can disrupt the balance of hormones involved in regulating various bodily functions, including those related to muscle contraction and relaxation. Hormonal imbalances can trigger or exacerbate cramps, making stress reduction crucial in maintaining the harmonious functioning of these systems.

By actively engaging in stress-reducing activities such as mindfulness, relaxation techniques, or exercise, individuals can positively influence their hormonal balance and alleviate muscle tension. This proactive approach not only lessens the likelihood of cramps but also promotes overall well-being. Creating a stress-free environment contributes to a healthier physiological state, making the body more resilient and less prone to experiencing discomfort, spasms, or cramps.
Maintain Electrolyte Balance
Maintaining electrolyte balance is crucial in preventing muscle cramps due to these charged minerals’ essential role in muscle function. Electrolytes, including potassium, magnesium, and calcium, contribute to the intricate dance of signals between nerves and muscles. Here’s why maintaining electrolyte balance is key to cramp prevention.
Electrolytes help regulate the nerve impulses that control muscle contractions and relaxations. An imbalance can lead to erratic signals, increasing the likelihood of involuntary muscle cramps.
Electrolytes work hand-in-hand with fluids to maintain proper cell hydration. When there’s an electrolyte imbalance, cells may not retain water effectively, leading to dehydration. Dehydrated muscles are more prone to cramping.
Potassium’s Role: Potassium is particularly vital for muscle function, playing a central role in maintaining the electrical potential of muscle cells. An insufficient supply of potassium can result in muscle weakness and cramps.
Magnesium contributes to muscle relaxation after contraction. A magnesium deficiency may result in prolonged muscle contractions, increasing the risk of cramps.
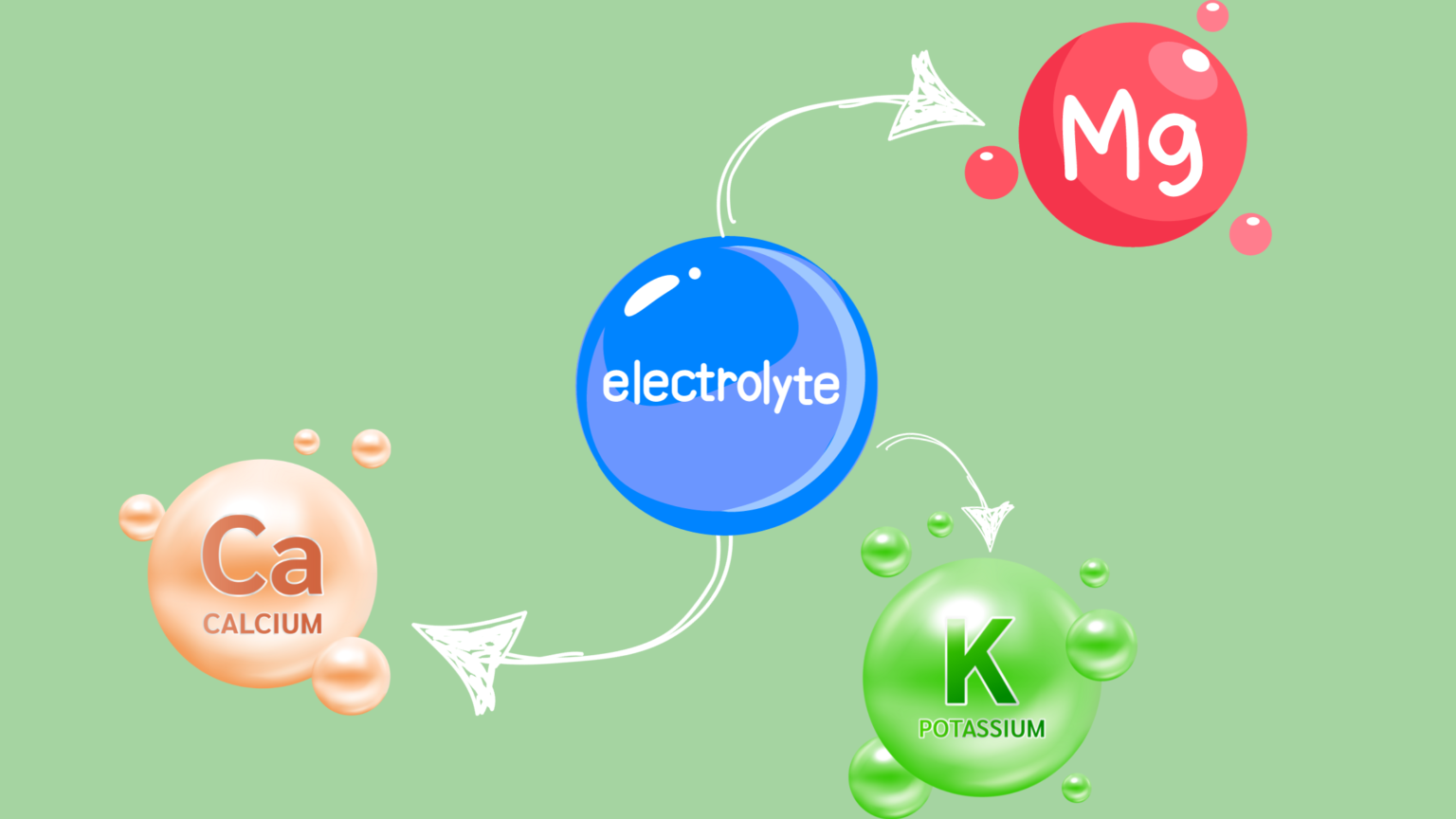
Calcium is essential for the initiation of muscle contractions. An adequate supply of calcium ensures proper signaling, preventing muscles from contracting excessively and causing cramps.
Intense physical activity, especially in hot conditions, leads to the loss of electrolytes through sweat. Replenishing these electrolytes becomes crucial to avoid imbalances that could trigger muscle cramps.
Electrolytes help prevent neuromuscular fatigue, a condition where the communication between nerves and muscles becomes less efficient. Fatigued muscles are more susceptible to cramps.
Proper electrolyte balance contributes to optimal blood circulation. Efficient blood flow ensures that muscles receive the oxygen and nutrients they need, reducing the likelihood of cramping.
Proper Footwear
Proper footwear provides adequate arch support, which helps distribute the body’s weight evenly across the feet. This support reduces strain on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments, minimizing the risk of cramps caused by overexertion.
Quality footwear often comes with effective shock absorption features. This helps absorb the impact of each step during activities like walking, running, or exercising. Reduced impact means less stress on the muscles, decreasing the likelihood of cramps.
Well-designed shoes offer stability and balance, preventing excessive pronation (inward rolling of the foot) or supination (outward rolling). Maintaining proper alignment of the foot and ankle reduces the strain on muscles and helps prevent cramps.
Shoes with an appropriate toe box size prevent compression of the toes and allow natural movement. When toes are cramped or compressed, it can lead to muscle imbalances and increase the risk of cramps, especially during prolonged periods of standing or walking.
Shoes that fit correctly prevent friction, blisters, and unnecessary pressure points. A snug but comfortable fit ensures that the foot is adequately supported, reducing the chances of muscle cramps caused by discomfort or rubbing.

Adequate ventilation in footwear helps maintain a dry and comfortable environment for the feet. Damp conditions can contribute to muscle cramps, so well-ventilated shoes play a role in preventing these issues.
Different activities require different types of footwear. Choosing shoes designed for the specific activity you’re engaging in ensures that your feet are adequately supported and protected, reducing the risk of cramps associated with improper footwear.
For activities that involve lateral movements or uneven terrain, footwear with proper ankle support is crucial. This support helps stabilize the ankle joint and surrounding muscles, preventing cramps caused by sudden twists or turns.
The materials used in the construction of footwear impact its overall performance. Quality materials provide durability and support, contributing to the prevention of muscle fatigue and cramps.
Over time, the supportive features of footwear wear out. Regularly replacing worn-out shoes ensures that you continue to benefit from proper support, reducing the risk of muscle cramps associated with inadequate footwear.
Sleeping position
Certain sleeping positions, particularly those that allow for better spinal alignment, can promote muscle relaxation. When muscles are in a more neutral position, it may reduce the likelihood of cramps, especially in areas like the legs.
Stretching Before Sleep: Some individuals find that incorporating gentle stretching exercises before bedtime can help prevent cramps during the night. Stretching can release tension in the muscles and improve flexibility, potentially reducing the risk of cramping.

Leg Elevation: Elevating your legs slightly while sleeping can promote better blood circulation and reduce strain on the lower limbs. Improved circulation can contribute to muscle health and potentially decrease the occurrence of cramps.
Supportive Pillows: Proper support for your head and neck with the right pillow can help maintain a more comfortable sleeping position. This can indirectly contribute to overall muscle relaxation, potentially reducing the likelihood of cramps.
What causes hamstring cramps at night?
Hamstring cramps at night can be caused by factors such as dehydration, overexertion, poor blood circulation, electrolyte imbalances, inadequate stretching, nerve disorders, medication side effects, pregnancy, and age-related changes. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for persistent or severe cramps to identify the specific cause and determine appropriate prevention and relief strategies.
What is the best thing to prevent cramps?
The best approach to prevent cramps involves a combination of staying well-hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet with sufficient electrolytes (potassium, magnesium, calcium), warming up before exercise, regular stretching, using proper footwear, and avoiding overexertion. Individual factors may vary, so it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on preventing cramps based on your specific needs and health status.
What are 5 common causes of muscle cramps?
The five common causes of muscle cramps include dehydration, overexertion, electrolyte imbalances (specifically low potassium, magnesium, or calcium levels), poor blood circulation, and nerve compression or disorders (such as sciatica or lumbar radiculopathy). Understanding and addressing these factors through hydration, proper nutrition, adequate warm-up, and medical attention when necessary can contribute to preventing and alleviating muscle cramps.

How long do muscle cramps last?
The duration of muscle cramps can vary widely. In many cases, muscle cramps are brief and may last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. However, severe cramps or those associated with underlying medical conditions might persist for a longer duration or recur frequently. Factors such as the cause of the cramp, hydration status, muscle fatigue, and whether appropriate measures are taken for relief can influence the duration. If you experience persistent or severe cramps, it’s advisable to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and guidance.
What food to avoid if you have leg cramps?
If you experience leg cramps, consider avoiding or limiting certain foods and factors that may contribute to cramping. Highly processed foods, lacking essential nutrients, can lead to imbalances and cramps. Excessive sugar intake, found in sugary snacks and beverages, may contribute to inflammation and dehydration. High caffeine intake, commonly found in caffeinated beverages, can also lead to dehydration and an increased risk of cramps. Alcohol consumption can dehydrate the body and potentially disrupt electrolyte balance. Excessive salt intake from salty foods can contribute to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, increasing the likelihood of cramps.
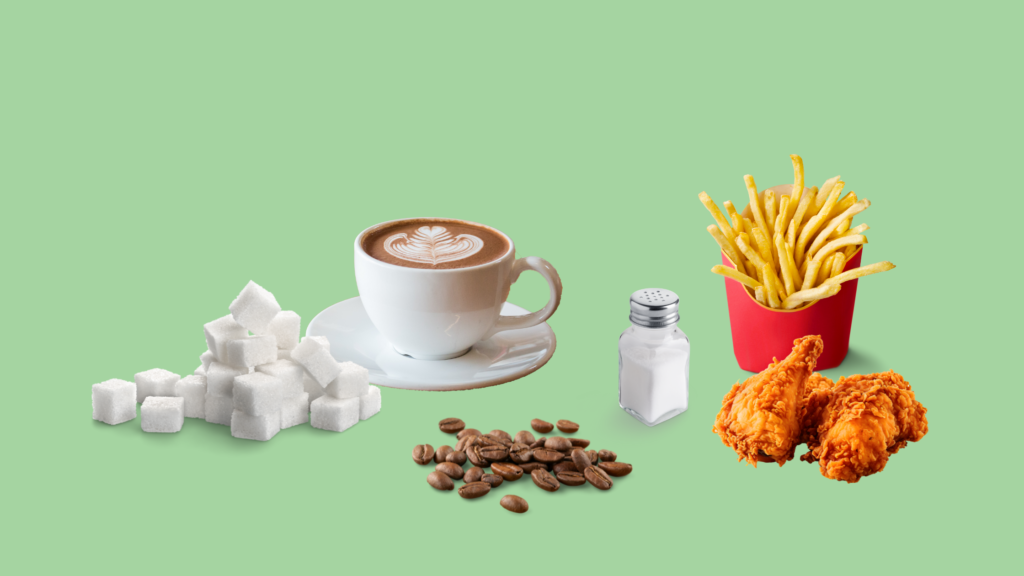

Fried and fatty foods may contribute to inflammation, potentially worsening muscle discomfort. While not a specific food, lack of hydration is a crucial factor; inadequate fluid intake can lead to dehydration and an elevated risk of cramps. It’s essential to maintain a balanced diet, stay well-hydrated, and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on your health status and nutritional needs.
Looking for Something else?